With the rise of remote work, routers are gaining more attention. Remote work opens the possibility for hackers to breach corporate security by abusing old and unpatched home routers, according to Atlas VPN. Router flaws may expose individuals and corporate networks to cybersecurity dangers such as hacking, data breaches, financial fraud, industrial espionage and others.
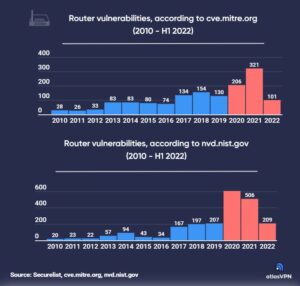 According to cve.mitre.org, there were 321 router vulnerabilities in 2021, the highest in over a decade. However, the increase in router vulnerabilities started the year before, when flaws jumped from 130 in 2019 to 206 in 2020, representing a growth of 58%.
According to cve.mitre.org, there were 321 router vulnerabilities in 2021, the highest in over a decade. However, the increase in router vulnerabilities started the year before, when flaws jumped from 130 in 2019 to 206 in 2020, representing a growth of 58%.
Citing data from the National Institute of Standards and Technology, Atlas VPN says 2020 was actually the worst year for router flaws, with a total of 603 vulnerabilities, representing a 191% increase over 2019.
However, 2021 was not much better, as vulnerabilities remained alarmingly high.
Out of the vulnerabilities identified last year, 87 of them were marked as critical. Of these vital flaws, 29.9% remained unpatched and without updates of any kind from the vendors. According to Atlas VPN, 26% of the critical router flaws were acknowledged by the vendors but not fixed as of June 8, 2022.
These vulnerabilities are the doors that allow hackers to intrude a household or corporate network, which makes it easier for them to circumvent password security measures, execute third-party programs, skip authentication, send remote orders to the router or even deactivate it.
How to Protect your Home Wi-Fi Network From Router Security Flaws
To safeguard against router hacks at home, AtlasVPN recommends these cybersecurity best practices:
- Make your wireless network password unique and strong. Don’t use the wireless routers default password. Hackers may easily guess this default password, especially if they know the router manufacturer.
- Change the Default SSID. Change your WiFi network’s default name, usually known as the SSID. Leaving the default can show your router’s manufacturer and model.. You may also instruct your router to stop broadcasting the SSID entirely. To connect to WiFi using a new device, you must manually enter the network name rather than picking it from a list of nearby possibilities.
- Keep your router’s software up to date. Router firmware can have flaws that can lead to serious vulnerabilities if not immediately addressed by their makers’ firmware upgrades. It is vital to install the most recent software for your router and download the most recent security updates as soon as possible.
- Enable network encryption. Almost every wireless router has encryption. Most routers, however, have it turned off by default. Enabling the encryption setting on your wireless router might help safeguard your network.
If you enjoyed this article and want to receive more valuable industry content like this, click here to sign up for our digital newsletters!










Leave a Reply